Arterial Dissection
Summary
- Arterial dissection is characterized by a tear in the intimal layer of an artery, allowing blood to enter the vessel wall and create a false lumen
- Common locations include carotid, vertebral, and aortic arteries
- Imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosis and management
Pathophysiology
- Intimal tear allows blood to enter the media, creating a false lumen
- Propagation of dissection can lead to:
- Luminal narrowing or occlusion
- Aneurysmal dilatation
- Rupture
- Mechanisms:
- Spontaneous (e.g., connective tissue disorders)
- Traumatic (e.g., blunt or penetrating injury)
- Iatrogenic (e.g., catheterization procedures)
Demographics
- Incidence: 2.6-3.0 per 100,000 person-years for carotid dissection
- Age: Peak incidence in 40-50 years old
- Gender: Slight male predominance
- Risk factors:
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Connective tissue disorders (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
- Recent trauma or chiropractic manipulation
Diagnosis
- Clinical presentation:
- Headache or neck pain
- Neurological deficits (e.g., TIA, stroke)
- Horner's syndrome (in carotid dissection)
- Laboratory tests:
- D-dimer (elevated in acute dissection)
- Imaging:
- Essential for definitive diagnosis
Imaging
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA):
- First-line imaging modality
- High sensitivity and specificity
- Rapid acquisition
- Findings:
- Intimal flap
- Double lumen sign
- Mural thrombus
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA):
- Alternative to CTA
- No radiation exposure
- Findings:
- Intramural hematoma (T1 hyperintense crescent)
- Luminal narrowing or occlusion
- Ultrasound:
- Limited role in diagnosis
- Useful for follow-up of carotid and vertebral dissections
- Findings:
- Intimal flap
- Reversed flow in false lumen
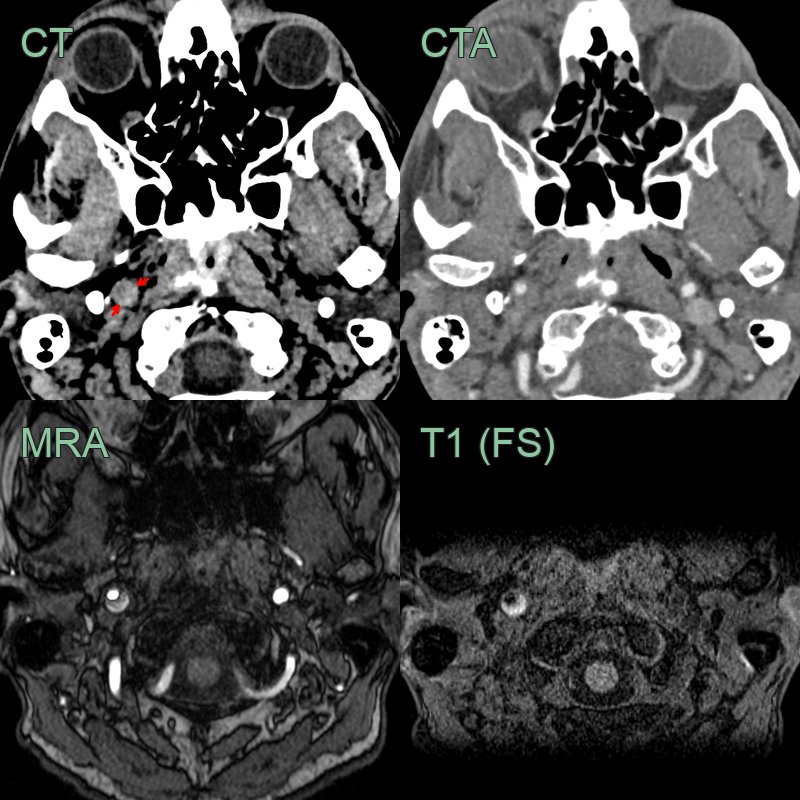
- 50-year-old patient presented with sudden onset right sided neck pain and a Horner's syndrome (blurred vision, right sided miosis and ptosis).
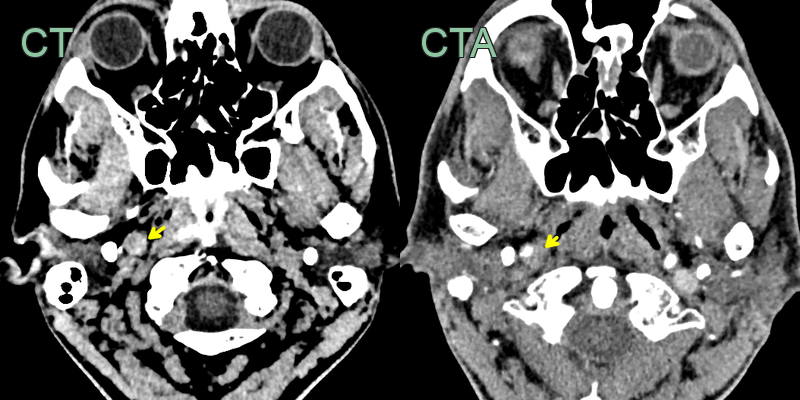
- The initial CT and CTA showed a hyperdense rim around an expanded right ICA below the skull base without a significant stenosis (yellow arrow).
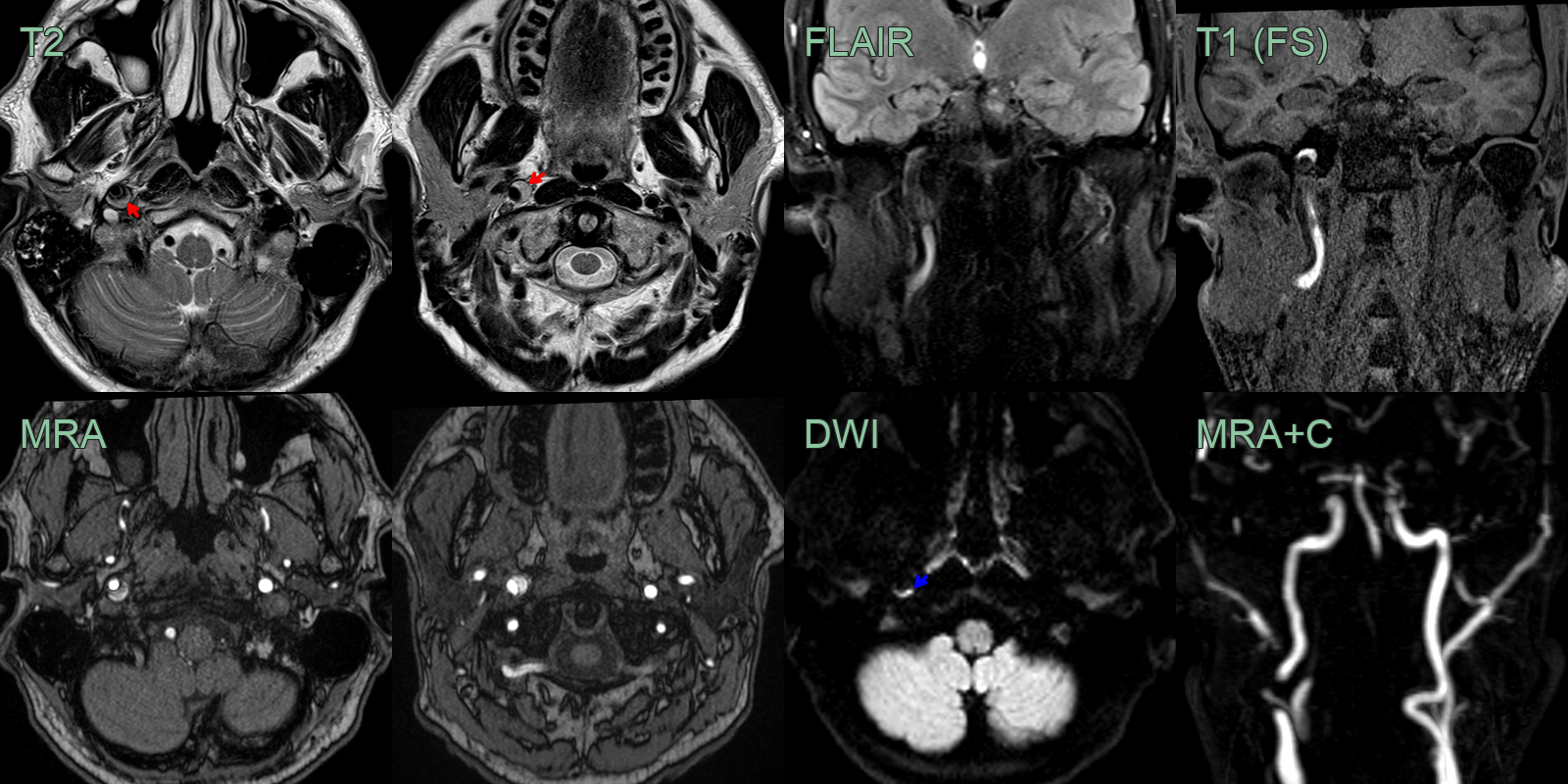
- The T1-weighted imaging showed a T1-hyperintense rim around the ICA (red arrow).
- The mural thrombus also showed diffusion restriction (blue arrow) and blooming on SWI (not shown).
Treatment
- Medical management:
- Anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy
- Blood pressure control
- Endovascular intervention:
- Stenting for flow-limiting dissections
- Coil embolization for pseudoaneurysms
- Surgical intervention:
- Reserved for cases refractory to medical/endovascular management
- Bypass grafting
- Vessel reconstruction
- Follow-up imaging:
- CTA or MRA at 3-6 months
- Ultrasound for carotid and vertebral dissections
Differential diagnosis
| Differential Diagnosis | Differentiating Feature |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerotic disease | Gradual onset, risk factors present, no intimal flap on imaging |
| Aneurysm | Focal dilatation, no intimal flap, often asymptomatic |
| Vasculitis | Systemic symptoms, inflammatory markers elevated, vessel wall thickening |
| Fibromuscular dysplasia | Beaded appearance on angiography, typically affects younger females |
| Traumatic vascular injury | Clear history of trauma, often associated with other injuries |
| Spontaneous intramural hematoma | No intimal flap, circumferential wall thickening |
| Arterial spasm | Reversible with vasodilators, no persistent imaging abnormalities |
| Thromboembolism | Sudden onset, identifiable embolic source, no intimal flap |
| Pseudoaneurysm | History of trauma or intervention, saccular outpouching on imaging |
| Arteriovenous malformation | Abnormal vessel tangle, arteriovenous shunting on imaging |